How to Install a DMG File on Ubuntu Ubuntu is a common variant of Linux, complete with a user-friendly interface and full flexibility in customising it via the Terminal window. Windows and Linux share the ability to open ISO files, which are similar to DMG files. From the next sub-menu that follows click on 'Open archive' and your DMG file will be opened and you can view the contents inside. Cons: You cannot view or extract files bigger than 4 GB. You cannot view or extract encrypted files. How to convert zip file into app. You are only allowed to extract 5 DMG files at a time. Way #2: Open DMG Files with DMG Extractor.
Recently I moved from Windows to Ubuntu on one of my laptops and since then I was trying to look for the way to create a VHDs or some sort of image files that I can use as a container. So I looked up for the solution and found a working solution scattered though places. So here I am putting it in a blog post to have all it in one place.
First we need to create an image file (.img) by using the dd command. The dd command is used to copy and convert the file. The reason it is not called cc is because it is already being used by C compiler. Here goes the command.

Note: The command execution time depends on the size of the image you have opted out for.
The if param stands for input file to refer the input file. As if, of stands for output file and this will create the .img file with the name you specify. The third param bs stands for block size. This will let you set the size of the image file. The G in the above command stands for GigaByte (GB). You can set the image size by specifying the block size. In this case G stands for GigaBytes (GB), K for KiloBytes (KB), T for TeraBytes (TB), P for Petabytes (PB) and so on. Here I am creating a 5 blocks of 1 GB each for the image file name cdata.
This command will create the .img file but you cannot mount this file as of yet. To do that you have to format the image so that it can have a file system. To do this make use of mkfs command.
I am creating an ext3 filesystem on my image file. -F is to force the operation. Here is the output of the command.
Now we can mount the image file by using the mount command:
With the success of the above command, you can see the image mounted on your desktop. You can unmount the image by clicking the eject or unmount button as shown in the below screenshot or you can execute the umount command to do that.
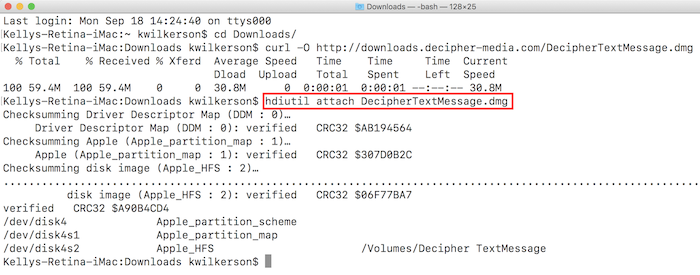
Note: The command execution time depends on the size of the image you have opted out for.
The if param stands for input file to refer the input file. As if, of stands for output file and this will create the .img file with the name you specify. The third param bs stands for block size. This will let you set the size of the image file. The G in the above command stands for GigaByte (GB). You can set the image size by specifying the block size. In this case G stands for GigaBytes (GB), K for KiloBytes (KB), T for TeraBytes (TB), P for Petabytes (PB) and so on. Here I am creating a 5 blocks of 1 GB each for the image file name cdata.
This command will create the .img file but you cannot mount this file as of yet. To do that you have to format the image so that it can have a file system. To do this make use of mkfs command.
I am creating an ext3 filesystem on my image file. -F is to force the operation. Here is the output of the command.
Now we can mount the image file by using the mount command:
With the success of the above command, you can see the image mounted on your desktop. You can unmount the image by clicking the eject or unmount button as shown in the below screenshot or you can execute the umount command to do that.
Open Ubuntu Files In Windows
How to play pokemon trading card game online. Unmounting the image by using command line.

